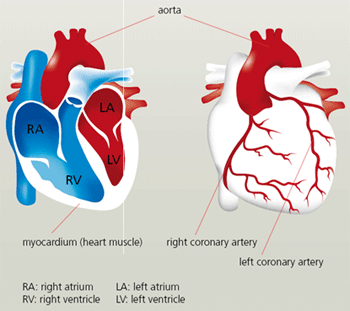
 Heart is a muscular organ present in the chest on the left side. The main function of heart is to pump blood to all organs of the body. Nearly 5 litres of blood is pumped by the heart per minute. The direction of the blood flow is controlled by four valves in the heart. Although blood passes through the heart it cannot get oxygen from it directly. Heart has its own set of arteries called coronary arteries which supply oxygen to the heart muscle. Both the coronary arteries and the valves can get affected by disease process. The blockage in the coronary arteries is called "Heart attack" and "Angina". It is possible to diagnose and treat these blockages by various tests. The best and gold standard is coronary angiogram. It is also possible to prevent the blockages by a good lifestyle as detailed in the following few paragraphs. These days you may must have heard terms like angiography, angioplasty and bypass surgery. These terms are explained in the following paragraphs. Heart is a muscular organ present in the chest on the left side. The main function of heart is to pump blood to all organs of the body. Nearly 5 litres of blood is pumped by the heart per minute. The direction of the blood flow is controlled by four valves in the heart. Although blood passes through the heart it cannot get oxygen from it directly. Heart has its own set of arteries called coronary arteries which supply oxygen to the heart muscle. Both the coronary arteries and the valves can get affected by disease process. The blockage in the coronary arteries is called "Heart attack" and "Angina". It is possible to diagnose and treat these blockages by various tests. The best and gold standard is coronary angiogram. It is also possible to prevent the blockages by a good lifestyle as detailed in the following few paragraphs. These days you may must have heard terms like angiography, angioplasty and bypass surgery. These terms are explained in the following paragraphs.
- Coronary angiogram
What is angiography?
Angiography is a diagnostic test which the doctors perform to check if any blockages have developed inside the arteries of your heart. The pictures show normal coronary arteries.
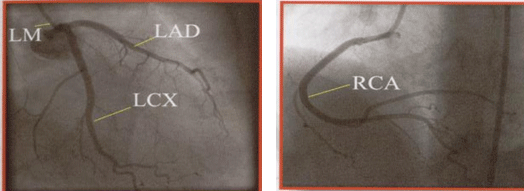 Who needs angiography?
Patients who develop heart attack, angina or severe breathing difficulties need coronary angiography. If ECG is abnormal or reports of Treadmill testing are abnormal, then also coronary angiography may be needed. There are several other reasons which the doctor will guide you.
How is coronary angiogram done?
Coronary angiogram is a simple procedure which is performed after at least 5 hours fasting. After some tests the patient is taken to Cath Lab. Coronary angiogram can be performed from the leg or the wrist. He is placed on a cardiac monitor. Local anaesthesia is given in the leg or the wrist and a catheter is passed into the heart. A dye is injected into the arteries of the patient and blockages are detected.
How long does it take?
The procedure generally takes 10-30 minutes in the Cath Lab. Thereafter, the patient has to lie on bed for 6 hours if it is performed from the leg and only 1 hour if performed from the wrist.
What are the risks in coronary angiogram?
Coronary angiogram is a very safe procedure if done by experienced operators and with due care. However all procedure carry some risk which are summarised below in decreasing frequency. The risk of complications are vary variable depending on the age, severity of disease, associated diseases and the emergency with which the procedure is performed. Please discuss with the doctor about likely risk in your case.
Who needs angiography?
Patients who develop heart attack, angina or severe breathing difficulties need coronary angiography. If ECG is abnormal or reports of Treadmill testing are abnormal, then also coronary angiography may be needed. There are several other reasons which the doctor will guide you.
How is coronary angiogram done?
Coronary angiogram is a simple procedure which is performed after at least 5 hours fasting. After some tests the patient is taken to Cath Lab. Coronary angiogram can be performed from the leg or the wrist. He is placed on a cardiac monitor. Local anaesthesia is given in the leg or the wrist and a catheter is passed into the heart. A dye is injected into the arteries of the patient and blockages are detected.
How long does it take?
The procedure generally takes 10-30 minutes in the Cath Lab. Thereafter, the patient has to lie on bed for 6 hours if it is performed from the leg and only 1 hour if performed from the wrist.
What are the risks in coronary angiogram?
Coronary angiogram is a very safe procedure if done by experienced operators and with due care. However all procedure carry some risk which are summarised below in decreasing frequency. The risk of complications are vary variable depending on the age, severity of disease, associated diseases and the emergency with which the procedure is performed. Please discuss with the doctor about likely risk in your case.
 |
Contrast induced renal failure |
2-5% (varies with kidney disease) |
 |
Allergic reactions |
~ 1% |
 |
Arrhythmias |
0.7-3% (various types) |
 |
Local vascular complications |
0.5% |
 |
Cardiac perforation |
rare |
 |
Stroke |
0.07% |
 |
MI |
0.05% |
 |
Death |
1 in 1000 cases (in serious cases only) |
Can the treatment be done along with coronary angiography?
Yes. If you permit the doctor to do angiogram and go ahead with ant possible treatment at the same sitting, it will save effort, time, contrast material, cost and discomfort to the patient. You should discuss with the doctor for such a possibility so that he can prepare the case accordingly.
What is the difference in doing coronary angiogram from the wrist as opposed to the leg?
Both the procedures give the same information. However patient discomfort is less and recovery is faster when performed from the wrist. However the doctor should decide how to perform it. In general it is preferable to do it from the wrist.
Please feel free to consult your doctor to know more about it and to clarify any doubts before the procedure. Wish you all the best.
- Coronary angioplasty
What is angioplasty?
Angioplasty, also known as PTCA and Stenting, is a type of treatment which the doctor performs to clear any blockages which have developed inside the arteries of patient's heart.
Who needs angioplasty?
Patients who develop heart attack, angina or severe breathing difficulties who are found to have blockages in heart arteries on coronary angiography need angioplasty. Those patients who have undergone bypass earlier may also need angioplasty if they have recurrence of angina.
How is Coronary angioplasty done?
The doctor prepares the patient with some blood tests and starts some specific medications. Before coronary angioplasty a coronary angiogram is performed to locate the blockage. Just like coronary angiogram, coronary angioplasty can be performed from the leg or the wrist. After placing on a cardiac monitor, local anaesthesia is given in the leg or the wrist and a catheter is passed into the heart. A dye is injected into the arteries of the patient to locate the blockage. The blockage is opened with a balloon and a stent is placed at the site of blockage to keep it open.
What is complex angioplasty?
All blockages in the artery do not in the same way. Some blockages are severe, calcified, tortuous and (or) may involve side branches which the angioplasty more difficult and challenging. Such patients may need additional instruments like multiple stents and balloons, intravascular ultrasound, rotablation and some other additional hardware. Doctor will explain any such specific requirements to you.
How long does it take?
The procedure time is highly variable depending upon the complexity of the case but generally takes 30-60 minutes in the cath Lab. Complex angioplasty may take upto 3-4 hours as well. Thereafter the patient has to lie in bed for 6 hours if it is performed from the leg and only 1-2 hour if performed from the wrist.
What are the risks in coronary angioplasty?
Coronary angioplasty has become a very safe procedure if done by experienced operators and with due care. However all procedures carry some risk which are summarised below in decreasing frequency. The risk of complications are vary variable depending on the age, severity of disease, complexity of the blockage, associated diseases and the emergency with which the procedure is performed. Please discuss with the doctor about likely risk in your case.
 |
Contrast induced renal failure |
3-9% (varies with kidney disease) |
 |
Severe Allergic reactions |
~ 1% |
 |
Arrhythmias |
0.7-3% (various types) |
 |
Local vascular complications |
0.5-3% |
 |
Coronary perforation |
0.1% for simple angioplasty Upto 0.5-1% for CTO. Rotablation and calcified |
 |
Stroke |
0.07% |
 |
QMI |
1.0% |
 |
Non QMI (enzyme rise) |
10-30% |
 |
Death |
1 in 1000 cases (in serious cases only) Complications due to Anti-coagulation regime |
 |
Groin hematoma |
5% |
 |
Retroperitoneal hematoma |
1% |
 |
Heparin induced thrombocytopenia |
1% |
Can the treatment be done along with coronary angiography?
Yes. If you permit the doctor to do angiogram and go ahead with any possible treatment at the same sitting, it will save effort, time, contrast material, cost and discomfort to the patient. You should discuss with the doctor for such a possibility so that he can prepare the case accordingly.
What is the difference in doing coronary angioplasty from the wrist as opposed to the leg?
Both the procedures give the same result. However patient discomfort and some complications less and recovery is faster when performed from the wrist. However the doctor should decide how to perform it. In general it is preferable to do it from the wrist.
Please feel free to consult your doctor to know more about it and to clarify any doubts before the procedure. Wish you all the best.
- Coronary Artery Bypass surgery (CABG)
What is bypass surgery?
Bypass surgery is an operation where the cardiac surgeon opens the chest and puts new tubes to bypass the blocked arteries so that the blood flow to the deprived areas of the heart can be restored. The surgeon can put as many tubes as needed?
Who needs bypass surgery?
A patient who has severe or multiple blockages which cannot be cleared by angioplasty needs bypass surgery.
What tubes are used for bypass surgery?
Surgeon takes veins from the leg of the patient, artery from the left wrist or some arteries present in the chest called mammary arteries.
How long does it take to do bypass surgery?
Time of surgery depends upon various factors but usually it takes about 3-5 hours.
Is it safe to undergo bypass surgery?
Yes it is very safe to undergo bypass surgeryt. Modern science has made it very safe and effective.
How long does it take to recover from bypass surgery?
Typically, the patient is kept in the ICU for 24-48 hours and the in the ward for 5-7 days more. After discharge the patient gets back to normal life in next few weeks.
What are the complications of the bypass surgery?
Though bypass surgery is very safe but being a major surgery some complications like bleeding, infection, kidney disease, stroke and mental impairment can occur in a fraction of patients. All these can be predicted and managed well in most cases. Complications are seen in those cases who come very late or who have pre-existing diseases like stroke, kidney disease and diabetes.
What are the precautions after the bypass surgery?
Good health lifestyle of healthy diet and regular exercise is needed after bypass surgery. All medications prescribed by the doctor must be taken regularly. Diseases like high BP, diabetes and high cholesterol should be controlled aggressively. Meet the cardiologist every 3 months for complete care.
Diet and Exercise for a Healthy Heart?
Diet: Healthy diet can have all round good effect on health. Large number of risk factors of CHD like high BP, diabetes, high cholesterol and obesity can be improved by diet alone. First step towards healthy diet is to avoid over eating. A sedentary individual needs only 30 Kcal /Kg males of ideal body weight. The dietary measures for healthy eating are summarized below.
| Dietary Measure |
Purpose |
How to do it |
Beneficial effect |
Reduce salt
 |
Keeps BP under check |
Cut down on sauces, pickels, paapad etc and reduce topical salt in food |
BP remains normal and those on BP drugs need less drugs |
Cut down on oil
 |
Control on calories and therefore on weight, and to reduce cholesterol |
Each adult needs less than 1 liter oil per month. Modify cooking. Use stir frying, baking, roasting, steaming etc and avoid deep frying. Use Olive oil as much as feasible. |
-Keeps cholesterol in check because lot of oil is converted to cholesterol
-helps reduce weight |
Cut down on foods which contain high cholesterol
 |
To keep total dietary cholesterol less than 300 mg daily
 |
Avoid eating egg yolk, butter, Desi Ghee and prawns
 |
Low dietary cholesterol leads to reduced cholesterol in the blood |
Consume lots of fruits and vegetables
 |
Reduces fats in the blood, helps control BP and provides fiber |
Take upto 5 helpings of fruit daily. Best time to take fruits is empty stomach e.g. mid morning and evening time |
Reduces BP, cholesterol and blood sugar. Protects against constipation and many cancers |
Nuts
 |
Provide essential oils, trace elements |
30-40 gm (8-10 pieces) of nuts like walnut, almonds and cashew nuts |
Provide essential oils, trace elements |
Carbohydrates (sweets)
 |
Should be avoided in large quantities |
--- |
Too much sweets encourage weight gain and increase triglycerides in the blood. |
Alcohol
 |
Avoid it. But those who consume it can take in small quantities |
Beer 300 ml, Hard Liquor 60 ml, wine 150 ml daily. Excess of alcohol is dangerous for liver, nerves, brain, BP and diabetes |
Those who consume small amount have reduced chances of CHD |
Fish
 |
Provides Omega 3 fatty acids. |
200-300 gm fish per week |
Reduces cholesterol and triglycerides in the blood |
|
 Heart is a muscular organ present in the chest on the left side. The main function of heart is to pump blood to all organs of the body. Nearly 5 litres of blood is pumped by the heart per minute. The direction of the blood flow is controlled by four valves in the heart. Although blood passes through the heart it cannot get oxygen from it directly. Heart has its own set of arteries called coronary arteries which supply oxygen to the heart muscle. Both the coronary arteries and the valves can get affected by disease process. The blockage in the coronary arteries is called "Heart attack" and "Angina". It is possible to diagnose and treat these blockages by various tests. The best and gold standard is coronary angiogram. It is also possible to prevent the blockages by a good lifestyle as detailed in the following few paragraphs. These days you may must have heard terms like angiography, angioplasty and bypass surgery. These terms are explained in the following paragraphs.
Heart is a muscular organ present in the chest on the left side. The main function of heart is to pump blood to all organs of the body. Nearly 5 litres of blood is pumped by the heart per minute. The direction of the blood flow is controlled by four valves in the heart. Although blood passes through the heart it cannot get oxygen from it directly. Heart has its own set of arteries called coronary arteries which supply oxygen to the heart muscle. Both the coronary arteries and the valves can get affected by disease process. The blockage in the coronary arteries is called "Heart attack" and "Angina". It is possible to diagnose and treat these blockages by various tests. The best and gold standard is coronary angiogram. It is also possible to prevent the blockages by a good lifestyle as detailed in the following few paragraphs. These days you may must have heard terms like angiography, angioplasty and bypass surgery. These terms are explained in the following paragraphs.